Correlative light electron microscopy (CLEM)
The Wolfson Bioimaging Facility is specifically equipped to combine light and electron microscopy and to undertake CLEM experiments. By utilising the advantages of fluorescence microscopy (e.g. live cell imaging) with the higher resolution and contextual information which EM provides, CLEM can deliver considerably more information than either modality alone.
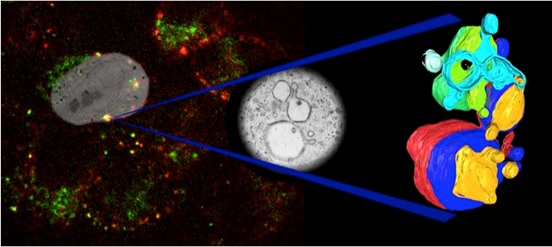
Recent papers including CLEM data:
- Hilditch, Romanyuk, Hodgson, Mantell, Neal, Verkade, Obexer, Serpell, McManus, Woolfson. Maturation and conformational switching of a de novo designed phase-separating polypeptide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c00256 (2024)
- Pope, Tanner, Masia, Payne, Arkill, Mantell, Langbein, Borri, Verkade (2023) Correlative light-electron microscopy using small gold nanoparticles as single probes.Light Sci Appl. 12(1)80
- Qiu, Buffonge, Ramnath, Jenner, Fawaz, Arkill, Neal, Verkade, White, Hezzell, Salmon, Suleiman, Welsh, Foster, Madeddu, Satchell (2022) Endothelial glycocalyx is damaged in diabetic cardiomyopathy: angiopoietin 1 restores glycocalyx and improves diastolic function in mice. Diabetologia. 2022 May;65(5):879-894.
- Baines, Yoshioka, Takuwa, Lane (2022) The ATG5 interactome links clathrin-mediated vesicular trafficking with the autophagosome assembly machinery. Autophagy Reports 1: 88-118
- Galloway, Bray, Shoemark, Hodgson, Coombs, Mantell, Rose, Ross, Morris, Harniman, Wood, Arthur, Verkade, Woolfson (2021) De novo designed peptide and protein hairpins self-assemble into sheets and nanoparticles. Small 17:e2100472
- Street, He, Jin, Hodgson, Verkade, Manners (2020) Cellular uptake and targeting of low dispersity, dual emissive, segmented block copolymer nanofibers. Chemical Science doi.org/10.1039/D0SC02593C
- Paul, Mantell, Borucu, Coombs, Surridge, Squire, Verkade, Dodding (2020) In situ cryo-electron tomography reveals filamentous actin within the microtubule lumen. Journal of Cell Biology 219: e201911154
