

Investigators and Projects
This figure summarises the autoimmune process. The table shows where specific
projects fit in this scheme. 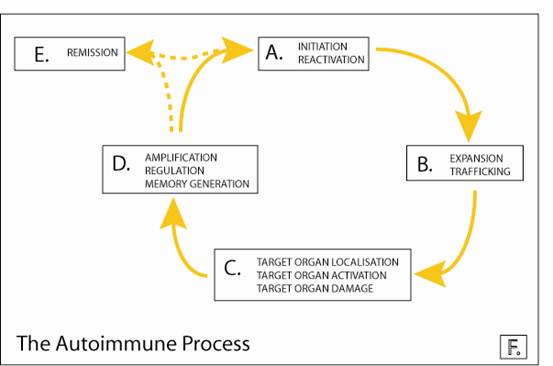
Process |
Mechanisms |
Projects |
A. |
Processing of autoantigens Recognition of autoantigens Cross-reactive activation (molecular mimicry) Balance of activating and inactivating signalling Costimulation Bystander activation |
Analysis of T cell responses to retinal autoantigens Role of macrophages as antigen presenting cells in the ocular environment |
B. |
Regulation of cell division Differentiation to effector phenotypes Chemotaxis and chemokinesis Endothelial/lymphocyte interactions |
Steroid control of lymphocyte responses Genesis and role of IL-17 specific T cells in EAU |
C. |
Extra-cellular matrix/cellular interactions Local antigen processing and presentation Actions of soluble mediators of inflammation Action of soluble mediators on lymphocytes and local tissue Repair of target organ damage |
Innate immune activation of macrophages Role of TNFR1, TLR-4 and TSP-1 in the regulation of ocular inflammation Role of complement in amplifying inflammatory responses Effects of inflammation on retinal repair |
D. |
Expansion and contraction of lymphocyte populations Generation of autoimmune specific regulatory cells Generation of autoantigen specific memory cells Epigenetic control of gene expression |
Lymphocyte population studies in EAU Epigenetic control of T cell activation status |
E. |
Loss of autoantigen specific lymphocytes Local down-regulation of inflammation Dominance of regulatory cells Effects of immune privilege Initiation of relapse |
Role of CD200/CD200R in the downregulation of inflammation |
F. |
Emergent properties that can arise in the context of the whole system | Computer simulations of simplified models of immune responses |