Feasibility Study
Objective
To test the Consultation Open and Close (COAC) intervention in a cluster-randomised framework to establish the feasibility both of the intervention and of a randomised control trial of the intervention.
Timescales
October 2020 – October 2021.
Participating practices
The six practices will be recruited in August 2020.
Methods
- Based on the results of the Intervention Development study, we will finalise the intervention.
- We will recruit six GP practices. Four of these will be randomly allocated to deliver the COAC intervention, and two will be randomly chosen as control practices (who will not deliver the intervention, but we will collect data from them for comparison purposes).
- Each practice will recruit 18 patients: 72 intervention and 36 control.
- We will collect quantitative data on the study outcome measures. We will also collect qualitative data from GPs, nurses, practice manager, administrators and receptionists and up to 30 patients.
- We will carry out a realist evaluation of the data to identify and understand the mechanisms by which any outcomes have occurred.
- We will analyse recruitment rates, follow-up rates, data completeness, and re-consultation rates within one/three months and other outcome measures to assess feasibility of a future randomised control trial.
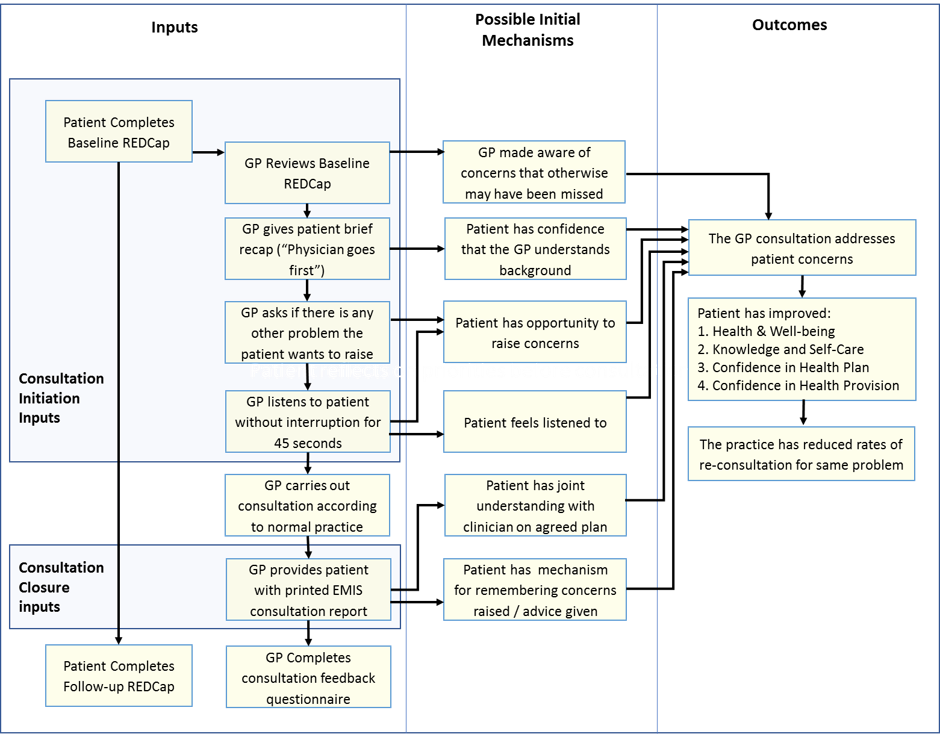
The COAC Intervention
The intervention is likely to comprise the following:
- PRE-CONSULTATION (PATIENT): Patients with an upcoming GP or nurse appointment receive a text that opens the pre-consultation questionnaire and invites them to complete this before the consultation.
- PRE-CONSULTATION (GP): The pre-consultation questionnaire report is delivered electronically to GPs/nurses before the consultation and clinicians review this information as well as patient history.
- CONSULTATION OPENING: At the start of the consultation, the GP/nurse greets the patient with a brief verbal synopsis of the patient’s recent medical history and pre-consultation form, and then invites the patient to speak without interrupting for up to 45 seconds. Following this, if the patient is still talking about the first presenting problem, the clinician may interrupt to refer to a second problem, if raised, or to ask, “is there some other problem or concern you want to discuss today”.
- CONSULTATION: Clinician carries out the consultation according to their normal practice.
- CONSULTATION CLOSURE: Clinician provides eligible patients with a written print-out of what was agreed in the consultation, including specific safety-netting advice.
The mechanism by which this is expected to work is shown in the programme theory below.