
WIRELESS BEND SENSOR (OFG)
 |
TECHNOLOGY:
WIRELESS BEND SENSOR (OFG) |
|

Even prototype technology can be
fun!
Plastic optical fibre is normally a good transmitter of light, but when it is bent, some light is lost. Using this 'bending loss' to advantage, an angle sensor (goniometer) can be constructed from a length of optical fibre that is fed by a light source at one end and measured by a compatible light detector at the other end. To create the Optical Fibre Goniometer (OFG) sensor in the CARESS project, the fibre has been looped (so that the emitter and detector sit next to each other), which allows all the electronics to be at one end of the sensor. With the sensor positioned across a joint, like the elbow, it can be used to detect the bend at the joint.

Final prototype of the optical
fibre bend sensor
with bend point towards the right and electronics off-right
Because of the greater mobility of children in mainstream schools, this sensor was integrated with a radio transmitter. Rather than have a belt-worn pack to plug sensors into, each sensor has its own transmitter, which means there is a total absence of wires. Each transmitter is tuned to its own frequency and has its own receiver, so multiple units can be used at the same time. (A Europe-wide licence-exempt frequency band was used around 434MHz.) Analogue modulation and narrowband FM were used to transmit the OFG signal, which is very close to DC.

The final prototype
wireless bend sensor
left: receiver box which plugs into the SoundBeam
right: OFG sensor embedded in fabric sleeve with transmitter and batteries

Lisa Percy assists a girl putting
on the wireless OFG sensor
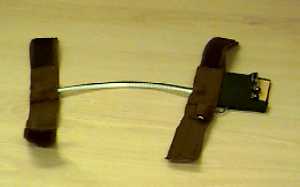
Early wired prototype of the OFG
Bend Sensor
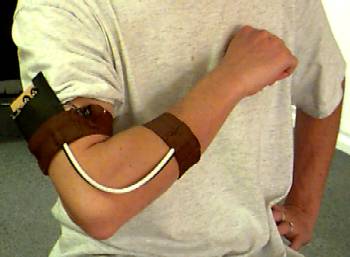
The wired bend sensor in use