
Radical Induced Ring Expansion of Tetramic Acids -
Access to Anti-Fungal Agents

Stage IV Project - Reshma Patel
Supervisor Dr Russell Cox
Second Assessor Dr G. C. Lloyd-Jones
Background
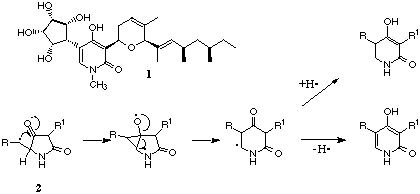
2-Pyridones are a comparatively rare class of secondary metabolites.
They are biologically formed by the condensation of a polyketide moiety
and an amino acid or its derivative. Compounds such as funiculosin 1
possess interesting biological functions such as anti-fungal and anti-tumour
properties. However functionalised 2-pyridones are extremely difficult
to synthesise. 2-Pyridones may be biosynthesised via radical induced
ring expansion of a tetramic acid 2, and this type of approach could
be put to use chemically. Precedence exists for similar chemical reactions
of carbocyclic molecules.
Programme
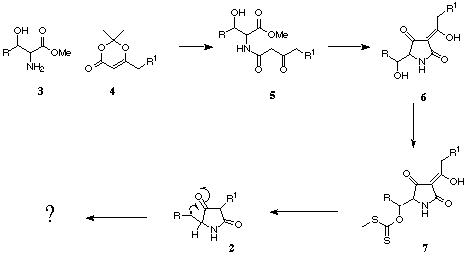
The synthesis of simple acyl tetramates bearing a hydroxyl functionality
at the beta-carbon was achieved last year by Stephen Cone by reacting beta-hydroxy
alpha-aminoesters 3 with acetone diketone adduct 4. The resulting
beta-keto amides 5 were cyclised easily to form acyl tetramates
6. This project will focus on the generation of a radical next to
the ring. This will be achieved by converting beta-alcohol 6 to
a methyl xanthate 7. Tin Hydride reaction will deoxygenate and generate
a radical at the required position. Characterisation of reaction products
will be undertaken to determine whether the required ring expansion has
occurred.
References
. Buck, J.; Madeley, J. P.; Pattenden, G. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans.
1, 1992, 67-73.
. Ito, K.; Miyajima, S. J. Heterocyclic Chem., 1992, 29, 1037-1044.
. Rigby, J. H.; Qabar, M. J. Org. Chem., 1989, 54, 5852-5853.
. Dowd, P.; Choi, S-C. Tetrahedron, 1989, 45, 77-90.
. Cone, S. P. Final Year Project, University of Bristol 1997.
. Nonhebel, D. C. Chem. Soc. Rev., 1993, 22, 347-359.
. Jones, R. C. F.; Tankard, M. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1991, 240-241.
. Barton, D. H. R.; Motherwell, W. B.; Stange, A. Synthesis, 1981, 743-745.